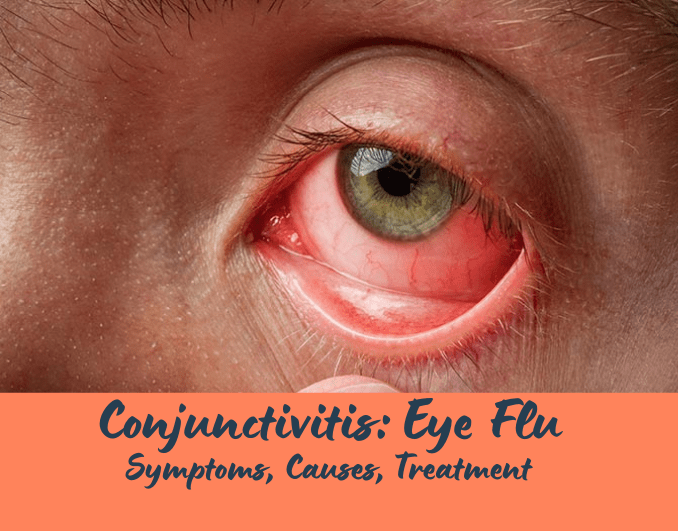
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as Pink Eye or Eye Flu, is a common eye condition that affects people of all ages. It is characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva, a thin, transparent layer that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inner surface of the eyelids. Conjunctivitis can be caused by various factors and may lead to discomfort and visual disturbances. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms, causes, and treatment of conjunctivitis, providing valuable insights to help you understand and manage this condition effectively.
Introduction
Conjunctivitis is a highly contagious eye condition that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, allergens, or irritants. It spreads easily, especially in crowded places, schools, and daycare centers. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for conjunctivitis is essential in managing the condition and preventing its transmission.
Types of Conjunctivitis(Eye Flu)
There are three primary types of conjunctivitis: viral conjunctivitis, bacterial conjunctivitis, and allergic conjunctivitis.
Viral Conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis is caused by various viruses, with Adenovirus being the most common culprit. Viral conjunctivitis starts in one eye and spreads to the other within a few days. Viral conjunctivitis is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct or indirect contact with infected eye secretions.
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pneumonia. It can result in significant eye discharge and may lead to crust formation on the eyelids. Bacterial conjunctivitis spreads through contact with infected hands or personal items.
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis occurs when the conjunctiva is exposed to allergens, such as pollen, pet dander, or dust mites. It is not contagious but can cause intense itching, redness, and tearing in both eyes.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of conjunctivitis can vary depending on the type of infection or irritant causing the condition. Some common symptoms include:
Redness and Swelling
The eyes may appear pink or red due to inflammation of the conjunctiva. Swelling of the eyelids may also be observed.
Itching and Irritation
Individuals with conjunctivitis often experience itching and a sensation of something foreign in the eye.
Excessive Tearing
Increased tear production is a common symptom of conjunctivitis, leading to watery eyes.
Discharge from the Eye
Bacterial and viral conjunctivitis may cause a sticky or watery discharge, often leading to crust formation around the eyes.
Sensitivity to Light
Conjunctivitis can make the eyes more sensitive to light, causing discomfort in bright environments.
Causes of Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis can be triggered by various factors. Some common causes include:
Viral Infections
Viral conjunctivitis is often associated with respiratory infections like the common cold.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial conjunctivitis can result from exposure to bacteria through contaminated hands or objects.
Allergens
Allergic conjunctivitis is triggered by the body’s immune response to allergens like pollen or pet dander.
Irritants
Chemicals or irritants in the environment can lead to irritant conjunctivitis.
Contact Lenses
Improper use or contaminated contact lenses can cause conjunctivitis.
Diagnosing Conjunctivitis
Diagnosing conjunctivitis typically involves a physical examination and a review of symptoms. In some cases, additional tests may be required.
Physical Examination
A healthcare professional will examine the eyes and ask about the symptoms and recent exposure to potential triggers.
Eye Swab Test
In cases of severe or persistent conjunctivitis, a swab of the eye discharge may be taken for laboratory analysis to identify the cause.
Allergy Testing
For allergic conjunctivitis, allergy testing may be recommended to determine the specific allergen triggering the condition.
Treating Viral Conjunctivitis
As viral conjunctivitis is typically caused by a virus, antibiotics are not effective in treating it. The condition usually resolves on its own within one to two weeks. However, there are ways to alleviate the discomfort and speed up recovery:
- Symptomatic Relief: Over-the-counter artificial tears can help soothe the eyes and alleviate dryness and irritation.
- Hygiene Measures: Practicing good hygiene is essential to prevent the spread of the infection. Avoid touching or rubbing the eyes, and wash your hands frequently, especially after touching the affected eye.
- Avoiding Contagion: Limit close contact with others to prevent the virus from spreading. It is advisable to stay home from school or work until the symptoms subside.
Treating Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis is often treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointments to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. Some additional measures to ease symptoms and promote healing include:
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected eye can help reduce swelling and loosen crusts.
- Hand Hygiene: Regularly washing hands and avoiding touching the eyes can prevent the spread of bacterial conjunctivitis.
Treating Allergic Conjunctivitis
The primary goal in managing allergic conjunctivitis is to avoid exposure to allergens. Additionally, the following treatments can provide relief from symptoms:
- Allergen Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding allergens that trigger the allergic reaction can significantly reduce symptoms.
- Antihistamine Eye Drops: Over-the-counter or prescription antihistamine eye drops can alleviate itching and redness.
- Lubricating Eye Drops: Artificial tears can help soothe the eyes and wash away allergens.
Home Remedies for Conjunctivitis
In addition to medical treatments, several home remedies can offer relief from conjunctivitis symptoms:
- Cold Milk Compress: Applying a cold milk compress to the eyes can reduce inflammation and soothe irritation.
- Aloe Vera Gel: The natural anti-inflammatory properties of aloe vera can help ease redness and discomfort.
- Chamomile Tea Bags: Placing cool, damp chamomile tea bags on the eyes can help reduce swelling and redness.
- Cucumber Slices: Cucumber slices have a cooling effect and can alleviate puffiness and irritation.
Preventive Measures
If you take some preventive measures, It can help reduce the risk of conjunctivitis:
- Handwashing: Frequent handwashing can prevent the spread of infections and bacteria.
- Avoiding Eye Rubbing: Refrain from touching or rubbing the eyes, as this can introduce irritants and lead to infections.
- Proper Contact Lens Care: If you wear contact lenses, ensure proper cleaning and hygiene to avoid infections.
- Regular Eye Checkups: Regular eye checkups can help detect conjunctivitis and other eye conditions early.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of conjunctivitis resolve on their own or with home remedies, some situations require prompt medical attention:
- Severe Pain: If you experience severe eye pain or sudden vision changes, seek medical attention immediately.
- Eye Injury: If you injure your eye, even if it appears minor, consult a healthcare professional.
- Prolonged Symptoms: If your symptoms persist or worsen despite home remedies, consult an eye specialist.
- High Fever: Conjunctivitis accompanied by a high fever may indicate a more severe infection that requires medical evaluation.
Conclusion
Conjunctivitis, or pink eye, is a common eye condition that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, allergens, or irritants. Identifying the type of conjunctivitis is essential for effective treatment and prevention of transmission. While viral conjunctivitis typically resolves on its own, bacterial and allergic conjunctivitis may require medical intervention. Practicing good hygiene, avoiding eye irritants, and seeking medical attention when necessary can help manage and prevent conjunctivitis effectively.
FAQs: Conjunctivitis: Eye Flu
Can conjunctivitis spread to both eyes?
Yes, conjunctivitis can initially affect one eye and spread to the other eye within a few days.
Is conjunctivitis contagious?
Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis are highly contagious and can spread through direct or indirect contact with infected eye secretions.
Can I wear contact lenses or avoid, if I have conjunctivitis?
It is best to avoid wearing contact lenses until the conjunctivitis has resolved to prevent further irritation and infection.
Are there any complications of conjunctivitis?
In most cases, conjunctivitis is a mild and self-limiting condition. However, in rare cases, it can lead to more severe complications if left untreated.
Can I use the same eye drops for viral and bacterial conjunctivitis?
No, it is crucial to use specific eye drops prescribed for the type of conjunctivitis you have, as viral and bacterial infections require different treatments.